Install Taskwarrior on Ubuntu 16.10
DeprecatedThis guide has been deprecated and is no longer being maintained.


Taskwarrior is an open source tool that manages tasks from the command line. Taskwarrior is blazing fast, written in C, updated frequently and available on practically every platform. This guide shows you how to install Taskwarrior on a Linode running Ubuntu 16.10.
Before You Begin
Familiarize yourself with our Getting Started guide and complete the steps for setting your Linode’s timezone.
This guide will use
sudowherever possible. Complete the sections of our Securing Your Server guide to create a standard user account, harden SSH access and remove unnecessary network services. Taskwarrior does not require opening ports in your firewall unless you choose to run it as a server daemon for multiple devices to connect to.Update your system:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Install Taskwarrior
Install Taskwarrior with the command:
sudo apt install task
After the packages are installed, run the command, task.
The system will ask if you want to create a configuration file for your user.
Answer yes.
You’ll find the sample configuration file at ~/.taskrc. To learn more about configuring task.rc, see the
official documentation.
Manage Tasks with Taskwarrior
You can manage your tasks and effectively use Taskwarrior with a handful of simple commands. Taskwarrior recommends spending time prioritizing your analog task list before applying the following commands to automate it.
Add a Task
To add a task, run the command, task add.
For example:
task add Add block storage volume to my Linode
will return:
Created task 1.
If you then run task again, you’ll see the job information. Taskwarrior assigns the newly added task an ID, and tracks the time elapsed since you ran the command.
taskwarrior@localhost:~$ task
[task next]
ID Age Description Urg
1 14s Add block storage volume to my Linode 0
1 task
You can add as many tasks as you want.
task add Attend Linux Users Group
Created task 2.
task add buy groceries
Created task 3.
Complete a Task
After you complete a task, you can mark it “done” using the [done] command (https://taskwarrior.org/docs/commands/done.html). The syntax is task <task_number> done.
taskwarrior@localhost:~$ task 1 done
Completed task 1 'Add block storage volume to my Linode'.
Completed 1 task.
Remove a Task
To remove a task you can run the task <task_number> delete command.
taskwarrior@localhost:~$ task 2 delete
Permanently delete task 2 'Attend Linux Users group'? (yes/no) yes
Deleting task 2 'Attend Linux Users group'.
Deleted 1 task.
Assign Tasks a Due Date
Using the due argument, you can assign a due date for a task:
task add write Taskwarrior guide for the Linode community due:tomorrow
taskwarrior@localhost:~$ task
[task next]
ID Age Due Description Urg
2 11s 7h write Taskwarrior guide for the Linode community 8.65
1 16min buy groceries 0
2 tasks
The due
argument allows a significant breadth for input. Read more about what’s possible with the due argument at
the official documentation.
Taskwarrior supports
recurring tasks by using the recur argument. The example below creates a daily task, the first of which is due 23 hours from the time of creation:
task add update ubuntu recur:daily due:daily
taskwarrior@localhost:~$ task
[task next]
ID Age Recur Due Description Urg
2 11min 7h write Taskwarrior guide for the Linode community 8.65
4 P1D 23h update ubuntu 8.34
1 28min buy groceries 0
3 tasks
Creating recurring task instance 'update ubuntu'
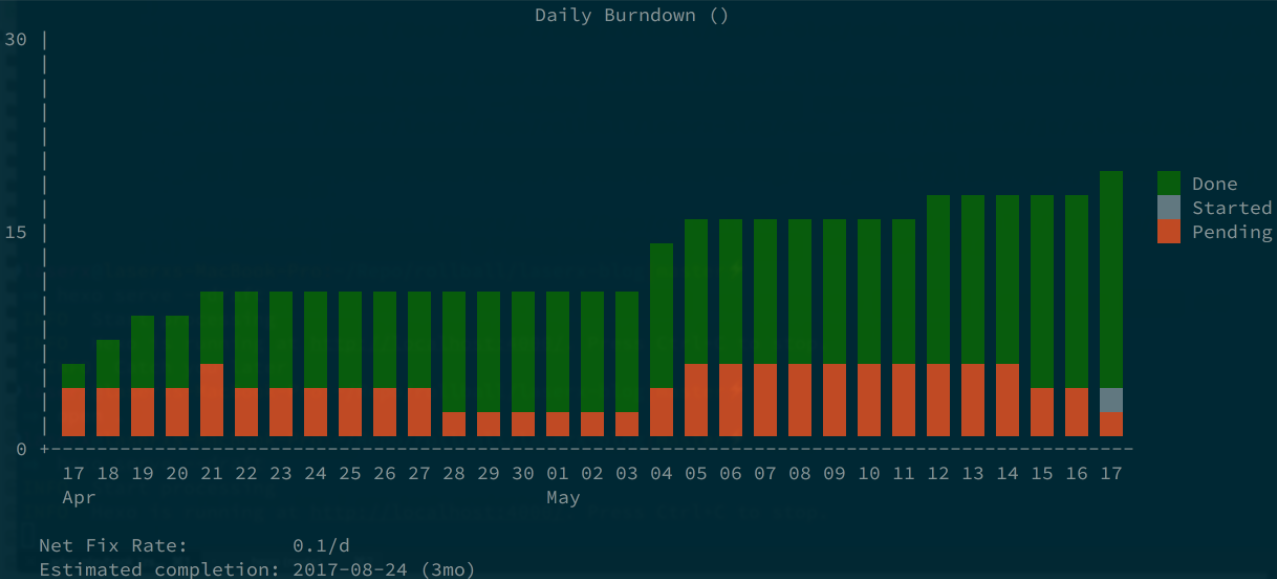
Visualization
Taskwarrior does much more than just list the tasks you’ve added on the command line. The burndown feature outputs graphical representations of your Taskwarrior workflow.


The calendar feature shows a calendar that contains all your tasks and due dates.

Next Steps with Taskwarrior
The next step to incorporate a Taskwarrior workflow into your life is to install task server on your Linode. Because Taskwarrior can be used across all your devices, including your phone, a central server in which to sync the data is needed. Taskwarrior offers do-it-yourself documentation on setting up such a task server:
Installing Taskserver.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on